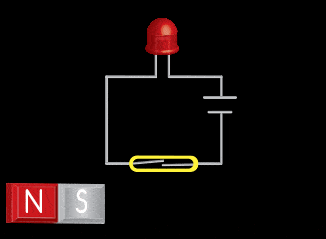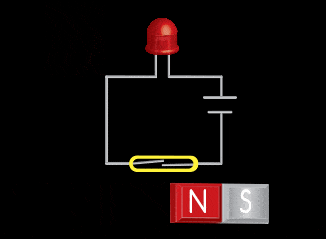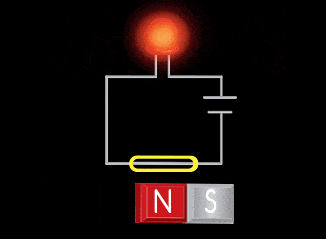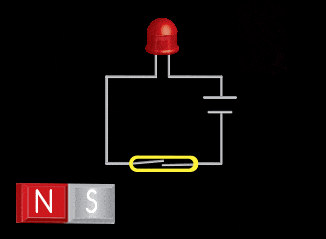
Permanent magnets are used to “trigger” magnetic sensors in a variety of applications. There are two main styles of magnetic sensor – the reed switch and the Hall Effect. Dura can provide a permanent magnet or turn-key package for integration into a sensor application.
Several parameters must be determined in order to select the proper magnet:
- Sensor style (Hall Effect or Reed)
- Trigger threshold (Hysteresis)
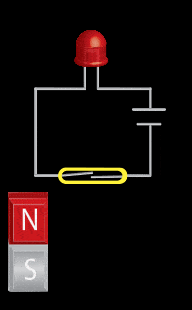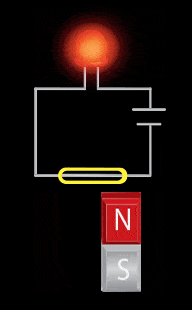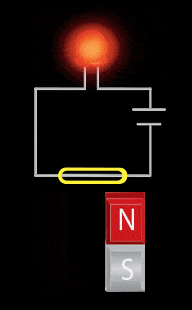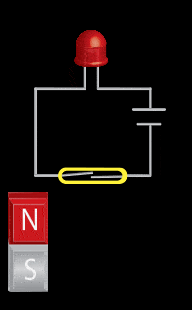
- Mechanical movement (Magnet relative to the sensor)
- Environmental conditions
- Dimensional requirements
- Proximity of flux biasing alloy
Hall Effect:
A Hall Effect sensor is usually an integrated circuit which utilizes the “Hall Effect” for detecting magnetic fields. The IC aspect of the sensor allows for a variety of output options and even a variable voltage out relative to the applied field strength. Some sensors are polarity dependent and as with the reed switch suffer from some hysteresis. Unlike the reed switch, the Hall Effect sensor will sense the magnetic flux which is normal (perpendicular) to the IC sensing face. This is usually a single defined plane on the sensor package.
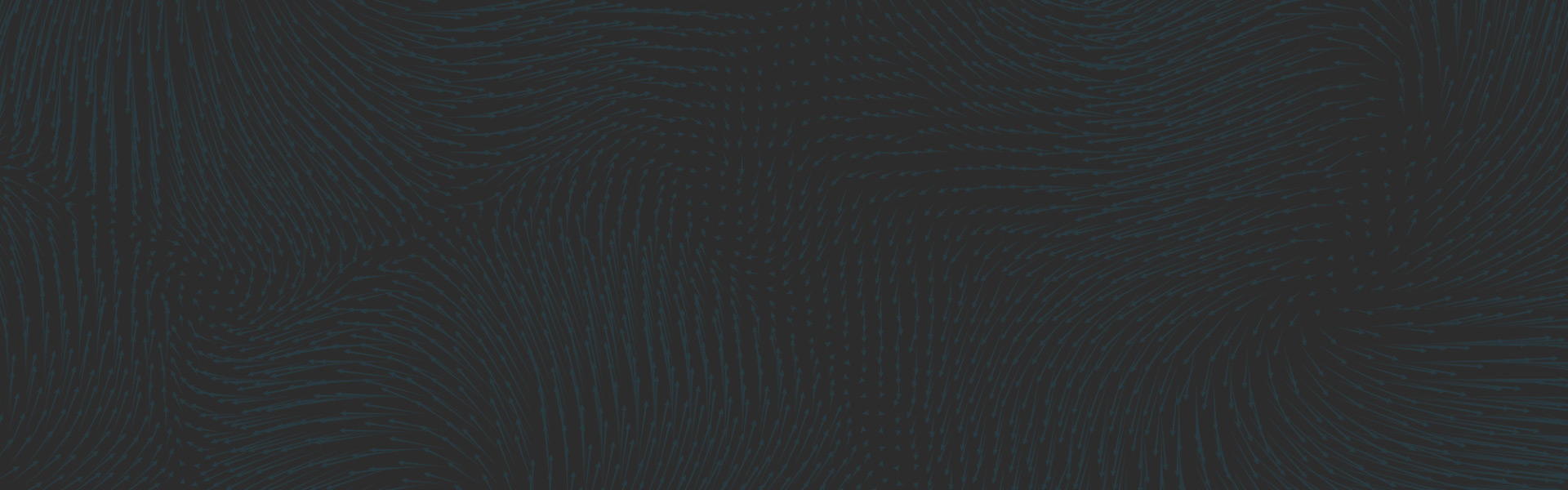
Reed Switch:
The reed switch utilizes two small soft-magnetic elements inside of a glass bulb. The elements change their continuity state in the presence of a magnetic field. A normally open reed switch will close when the proper magnitude and shape field is presented to it. This sensor makes use of the flux components running parallel to the bulb and soft-magnetic elements. This geometry usually requires the magnet to be oriented parallel to the bulb. Inaccurate triggering and “dead-spots” will be observed when utilizing a magnet oriented perpendicular to the bulb and elements.


ITAR Registered & Compliant
We are registered and compliant with the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR). This qualifies us to work with items listed on the United States Munitions List (USML). We are also ITAR registered with the Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC).